Email: szhou@henu.edu.cn
研究方向
围绕生物互作与农业生物安全,研究昆虫大量繁殖、环境适应与种群暴发机制,以及昆虫与植物、天敌和微生物的互作机理,发展绿色防控的新理论新技术新方法。
教育及工作经历
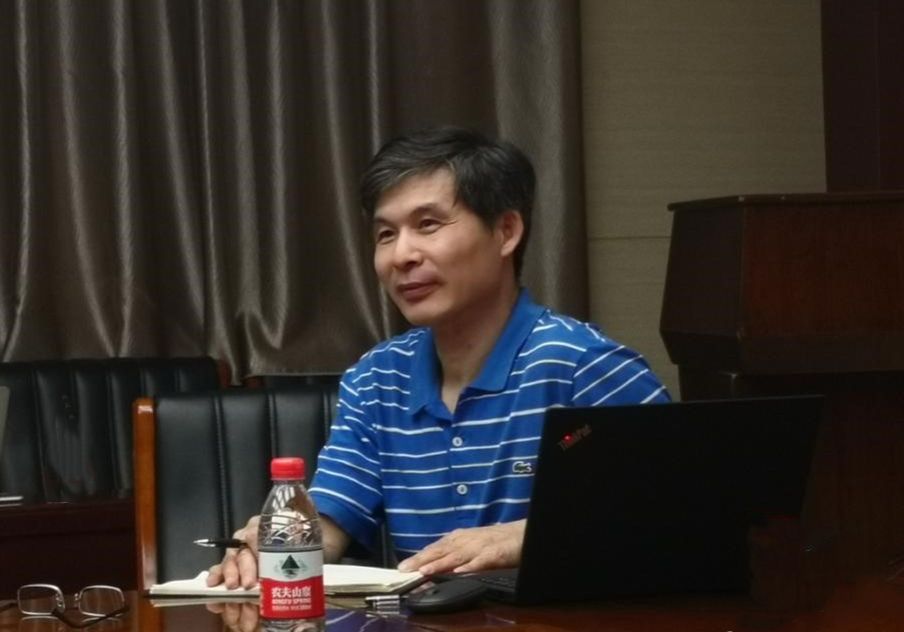
2002年毕业于加拿大皇后大学,获生物化学与分子生物学博士学位;2005-2010年美国杜克大学,助理教授,副研究员;2007-2009河南农业大学生命科学院,院长,特聘教授;2010-2015年中国科学院动物研究所,研究员,课题组长;2015-至今永利集团304am登录,棉花生物学国家重点实验室,教授,副主任,主任。
主要承担项目
1.国家自然科学基金重点项目:飞蝗对环境变化生殖适应的内分泌调控机制研究(31630070),2017.01-2021.12,277万元,主持。
2.国家自然科学基金NSFC-河南联合基金重点项目:群居型飞蝗迁飞的分子调控机制(U1804232),2019.01-2022.12,209万元,主持。
3.国家自然科学基金联合基金重点项目:内分泌激素协同调控飞蝗周期性大量产卵的分子机制(U22A20482),2023.01-2026.12,255万元,主持。
4.国家重点研发计划课题:蝗虫高生殖力机制与调节(2022YFD1400502),2022.09-2025.12,295万元,主持。
5.河南省重点研发计划:玉米害虫绿色防控技术集成研究与示范(221111112200),2022.01-2024.12, 200万元,主持。
教学与人才培养
《普通动物学》国家级线上一流本科课程,《高级生物化学》明德班本科双语课程,《生物学专业论文写作》和《生物学文献阅读》研究生课程,《昆虫的变态与生活史》虚拟仿真实验教学。
代表性论文(*通讯作者)
1.Jing Y, Wen X, Li L, Zhang S, Zhang C,Zhou S*. 2021. The vitellogenin receptor functionality of the migratory locust depends on its phosphorylation by juvenile hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 118(37): e2106908118.
2.Du E, Wang S, Luan YX, Zhou C, Li Z, Li N*,Zhou S*, Zhang T, Ma W, Cui Y, Yuan D, Ren C, Zhang J, Roth S, Li S*. 2022. Convergent adaptation of ootheca formation as a reproductive strategy in Polyneoptera. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 39(3): msac042.
3.Wu Z, Yang L, Li H,Zhou S*. 2021. Krüppel-homolog 1 exerts anti-metamorphic and vitellogenic functions in insects via phosphorylation-mediated recruitment of specific cofactors. BMC Biology. 19(1): 222.
4.Zheng H, Wang N, Yun J, Xu H, Yang J,Zhou S*. 2022. Juvenile hormone promotes paracellular transport of yolk proteins via remodeling zonula adherens at tricellular junctions in the follicular epithelium. PLoS Genetics. 18(6): e1010292.
5.Wu Z#, He Q#, Zeng B, Zhou H,Zhou S*. 2020. Juvenile hormone acts through FoxO to promote Cdc2 and Orc5 transcription for polyploidy-dependent vitellogenesis. Development. 147(18).
6.Song J,Zhou S*. 2020. Post-transcriptional regulation of insect metamorphosis and oogenesis. Cellular and Molecular Life Science. 77(10): 1893-1909.
7.Song J, Li W, Zhao H, Gao L, Fan Y,Zhou S*. 2018. The microRNAs let-7 and miR-278 regulate insect metamorphosis and oogenesis via targeting juvenile hormone early response gene Krüppel-homolog 1. Development. 2145(24).
8.Jing Y, An H, Zhang S, Wang N,Zhou S*. 2018. Protein kinase C mediates juvenile hormone-dependent phosphorylation of Na+/K+-ATPase to induce ovarian follicular patency for yolk protein uptake. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 293(52): 20112-22.
9.Wu Z, Guo W,Xie Y,Zhou S*. 2016. Juvenile hormone activates the transcription of Cell-division-cycle 6 (Cdc6) for polyploidy-dependent insect vitellogenesis and oogenesis. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 291(10): 5418-27.
10.Guo W, Wu Z, Yang L, Cai Z, Zhao L,Zhou S*. 2019. Juvenile hormone-dependent Kazal-type serine protease inhibitor Greglin safeguards insect vitellogenesis and egg production. The FASEB Journal. 33(1): 917-927.
11.Song J, Li W, Zhao H,Zhou S*.2019. Clustered miR-2, miR-13a, miR-13b and miR-71 coordinately target Notch gene to regulate oogenesis of the migratory locust Locusta migratoria. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 106: 39-46.
12.Zheng H, Chen C, Liu C, Song Q,Zhou S*. 2020. Rhythmic change of adipokinetic hormones diurnally regulates locust vitellogenesis and egg development. Insect Molecular Biology. 29: 283-292.
13.Wu Z, Guo W, Yang L, He Q,Zhou S*. 2018. Juvenile hormone promotes locust fat body cell polyploidization and vitellogenesis by activating the transcription of Cdk6 and E2f1. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 102: 1-10.
14.Zheng H, Zeng B, Shang T,Zhou S*. 2021. Identification of G protein-coupled receptors required for vitellogenesis and egg development in an insect with panoistic ovary. Insect Science. 28(4): 1005-1017.
15.Luo M, Li D, Wang Z, Guo W, Kang L*,Zhou S*. 2017. Juvenile hormone differentially regulates two Grp78 genes encoding protein chaperones required for insect fat body cell homeostasis and vitellogenesis. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 292(21): 8823-34.
16.Wang Z, Yang L, Song J, Kang L*,Zhou S*. 2017. An isoform of Taiman that contains a PRD-repeat motif is indispensable for transducing the vitellogenic juvenile hormone signal in Locusta migratoria. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 82: 31-40.
17.Guo W#, Wu Z#, Song J. Jiang F, Deng S, Walker VK,Zhou S*. 2014. Juvenile hormone-receptor complex acts on Mcm4 and Mcm7 to promote polyploidy and vitellogenesis in the migratory locust. PLoS Genetics. 10(10): e1004702.
18.Song J, Wu Z, Wang Z, Deng S,Zhou S*. 2014. Krüppel-homolog 1 mediates juvenile hormone action to promote vitellogenesis and oocyte maturation in the migratory locust. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 52: 94-101.
19.Ren D, Cai Z, Song J, Wu Z,Zhou S*. 2014. dsRNA uptake and persistence account for tissue-dependent susceptibility to RNA interference in the migratory locust, Locusta migratoria. Insect Molecular Biology. 23(2): 175–184.
20.Song J, Guo W, Jiang F, Kang L,Zhou S*. 2013. Argonaute 1 is indispensable for juvenile hormone mediated oogenesis in the migratory locust, Locusta migratoria. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 43(9): 879-887.